After a Mimosa (acacia dealbata) tree was felled, samples were collected from various places of its log and branches (thanks to D. Valentini for providing the log and branches). The tree had a 12″ main log up to about 8′ height. These samples were collected:
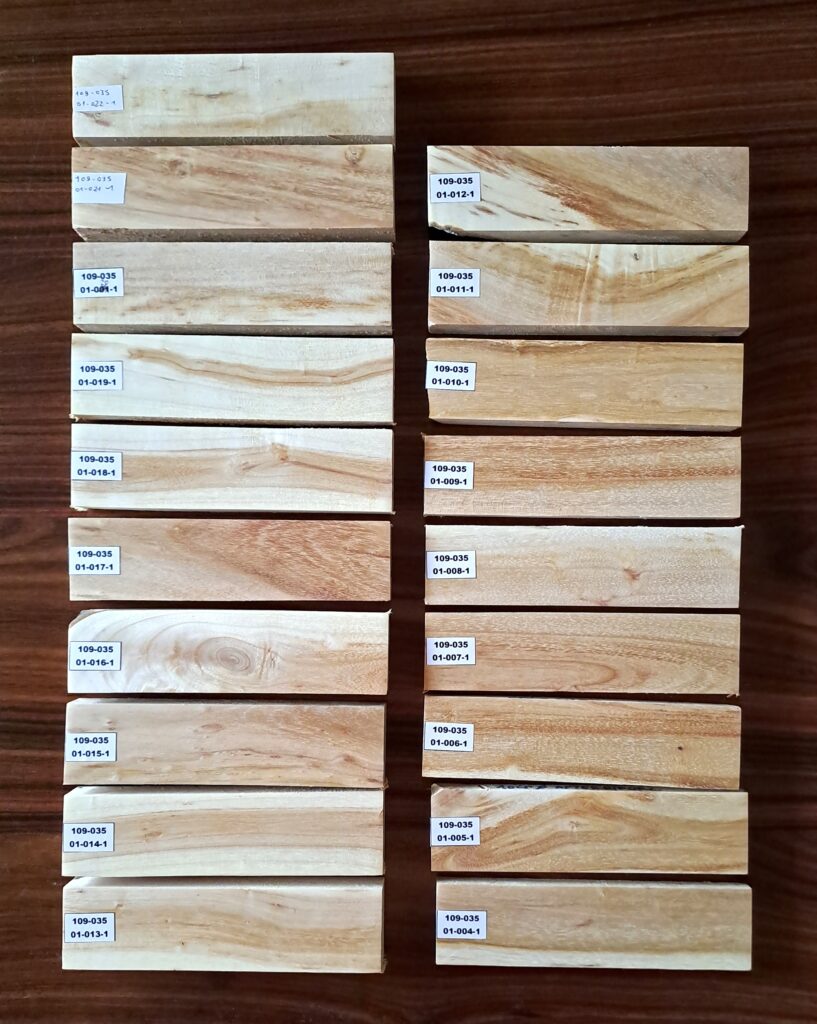
Table below summarizes the samples and the results:
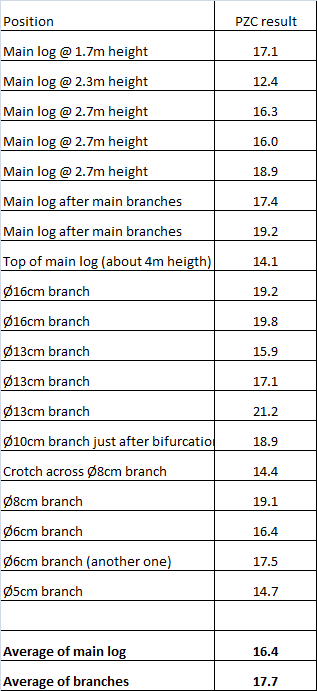
Interestingly, it appears that chatoyance can be found all around the tree, even in small branches, and in branches it is even higher than what is found in the main log.
Pictures below show what chatoyance looks like on each sample, with relevant notes. Since acacia dealbata sapwood is very light in color and also quite chatoyant, it can actually be “whiter than white” under some circumstances. For this reason all animated gifs have been deliberately darkened by 33%.



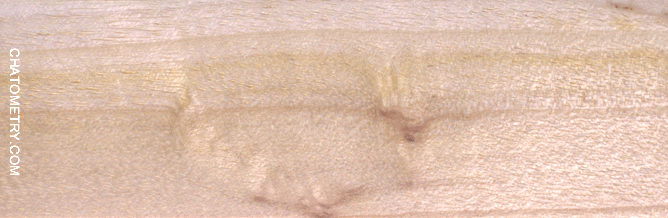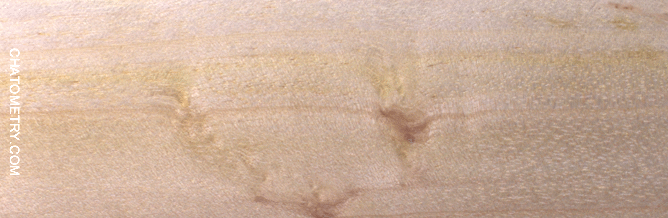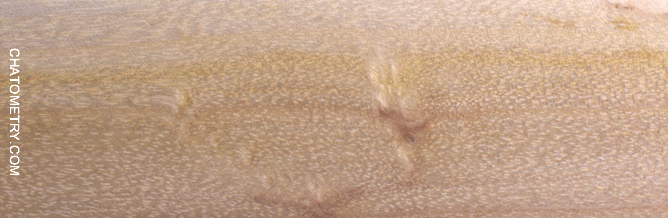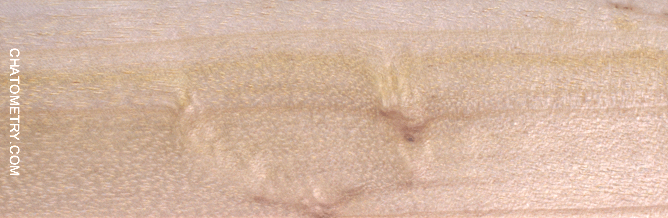















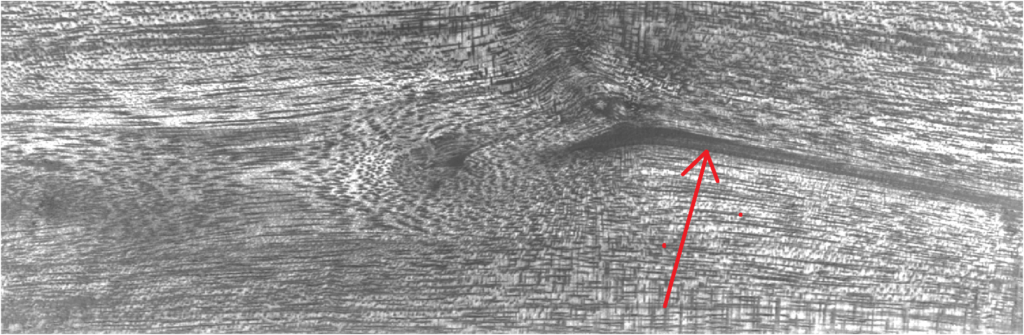
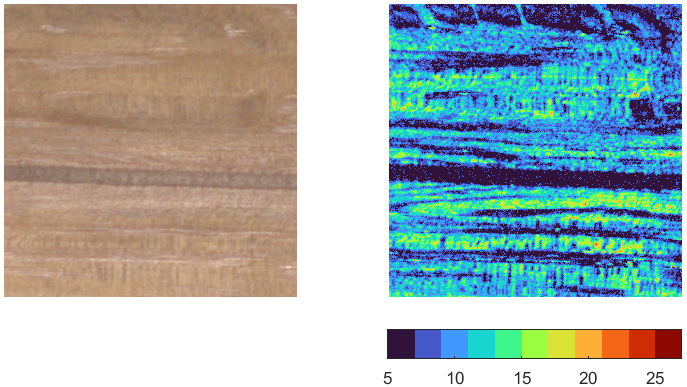
Some more info is worth adding: the last two sample shown above (Ø5cm branch and Ø6cm branch B) show the pith. In both the cases, the pith appears as less chatoyant than surround wood, as shown by the brightness anisotropy maps below:
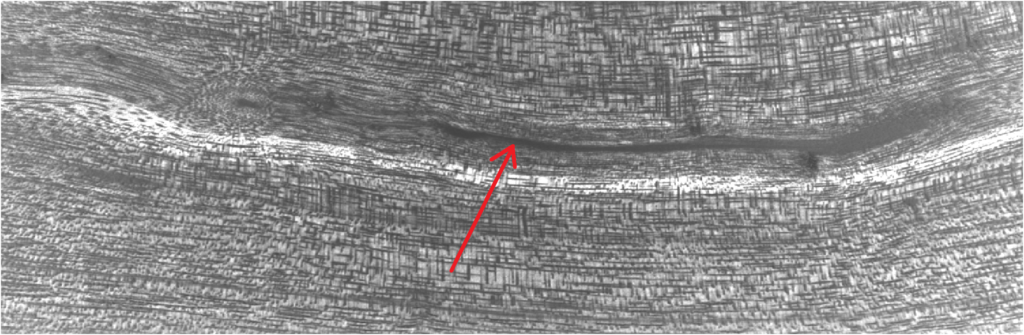
Chatoyance on the pith was also investigated on this Staghorn Sumac (rhus typhina) sample:

The pith area is clearly less chatoyant, even though something can be seen there too. This map provides better info:
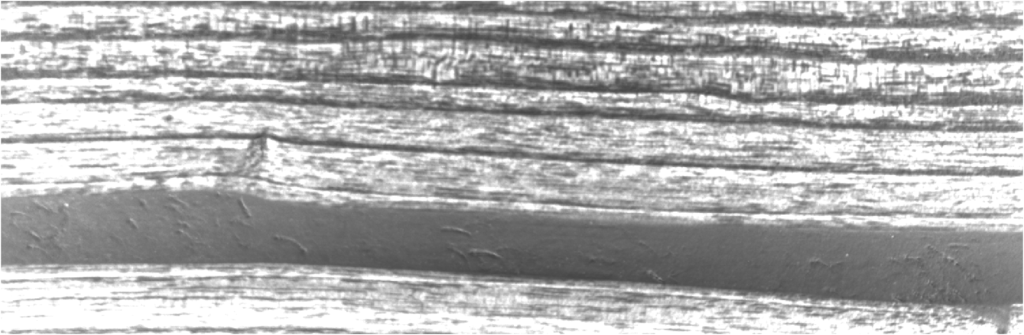
When looking at a detailed map it would seem that chatoyance is low but not zero on the pith:
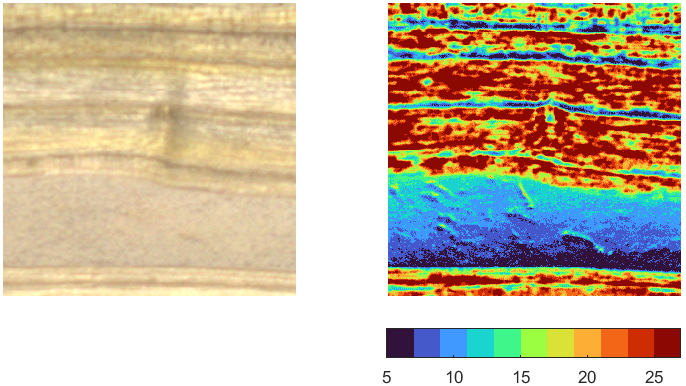
This Cork Oak sample also shows very low chatoyance on the pith:


Want to know more? Get Woodworker’s Guide to Chatoyance!

Available on Amazon in 12 countries – just click on your flag below…
… and enjoy the read!